But that is only the beginning of the story. The blood contains red blood cells RBCs white blood cells WBCs and platelets.
Types Of Tissues Anatomy And Physiology I
The specific functions of blood also include defense distribution of heat and maintenance of homeostasis.

. The function of this tissue is to separate blood from the fluid in tissues and to separate air from fluids in tissues and to filter substances from blood to form urine. What are the formed elements of blood. Study of blood and its disease is known as Hematology Composition of Blood.
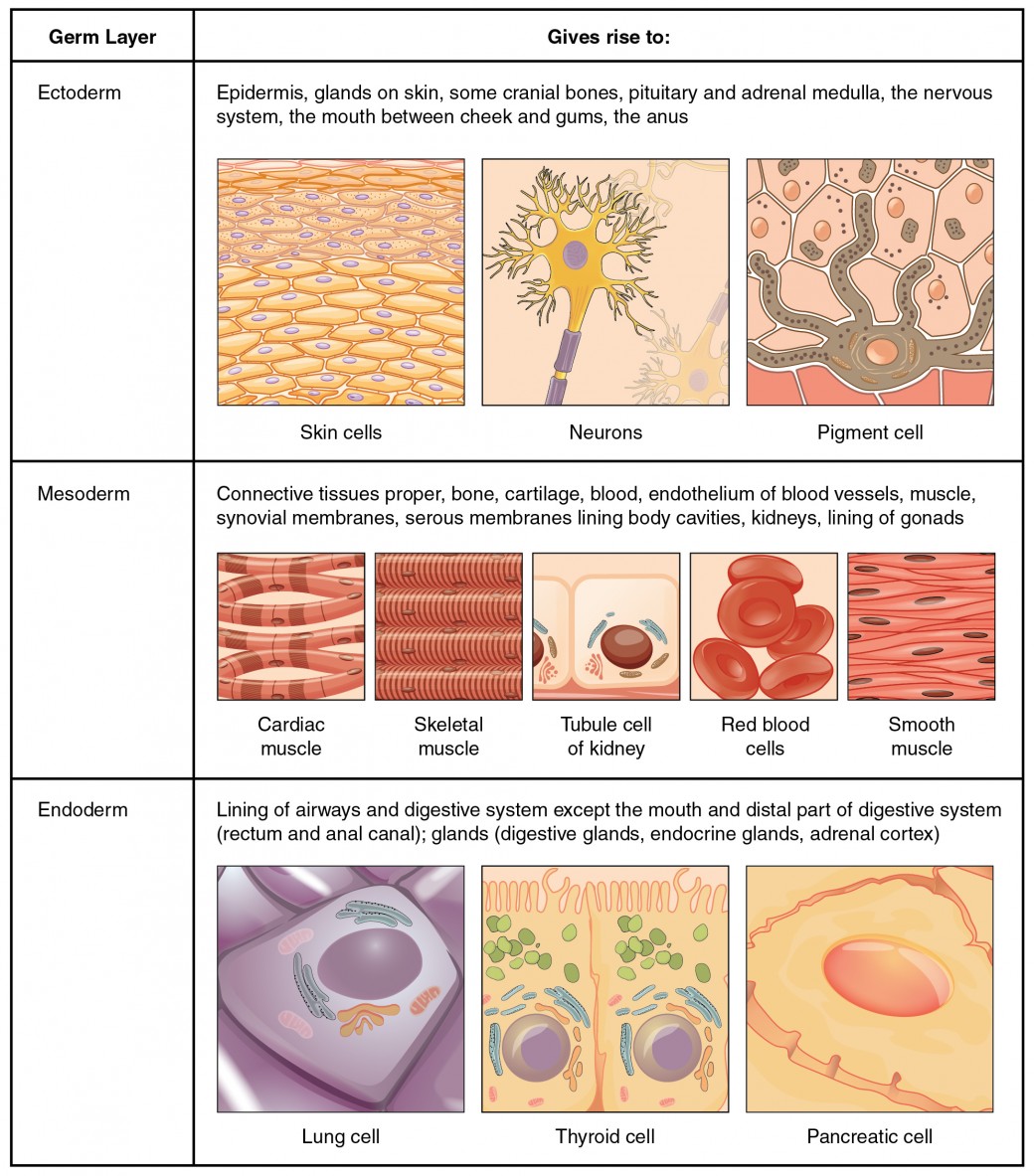
The four types of tissues in the body are epithelial connective muscle and nervous. It is a pale yellow coloured liquid in which various substances like food waste products hormones and gases remain in solution. Fibers form a loose framework stroma that support other cell types including white blood cells mast cells macrophages.
A tissue membrane is a thin layer or sheet of cells that covers the outside of the body for example skin the organs for example pericardium internal passageways that lead to the exterior of the body for example abdominal mesenteries and the lining of the moveable joint cavitiesThere are two basic types of tissue membranes. Blood plays a protective role by transporting clotting factors and platelets to prevent blood loss after injury. It transports the oxygen to cells throughout the body and it removes waste carbon dioxide from the cells.
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin which binds oxygen. The fluid extracellular matrix of blood is made up of plasma which constitutes slightly more than half of the tissue volume. Platelets are important for blood clotting.
Most organs contain all four tissue types. 1 Responsible for body movement 2 Moves blood food waste through bodys organs. What type of tissue is blood.
RBCs have haemoglobin and transport oxygen. For example the heart pumps blood the lungs bring in oxygen and eliminate carbon dioxide and the skin provides a barrier to protect internal structures from the external environment. Our tissues can be categorized into four major types.
The four types of tissue in the body are epithelial connective muscle and nervous. The next type of epithelial tissue is stratified squamous epithelium. Epithelial tissue is made of layers of cells that cover the surfaces of the body that come into contact with the exterior world line internal cavities and form glands.
To transport to different parts of the body. Blood which is a type of connective tissue develops from mesenchyme and consists of cells and cell derivatives that are immersed in a fluid intercellular substance plasma. Epithelial tissue is made of layers of cells that cover the surfaces of the body that come into contact with the exterior world line internal cavities and form glands.
Transportation Nutrients from the foods you eat are absorbed in the digestive tract. What are the major components of blood 3. Identify the four types of tissue in the body and describe the major functions of each tissue.
This is a tissue composed of two or more layers and the cells tend to be cuboidal. Identify the four types of tissue in the body and describe the major functions of each tissue. Define the term hematology.
Erythrocytes or red blood cells carry oxygen and carbon dioxide through the cardiovascular system. In the lungs the carbon dioxide moves from the blood to the air and is exhaled. Differentiated from both lymphoid and myleoid stem cells.
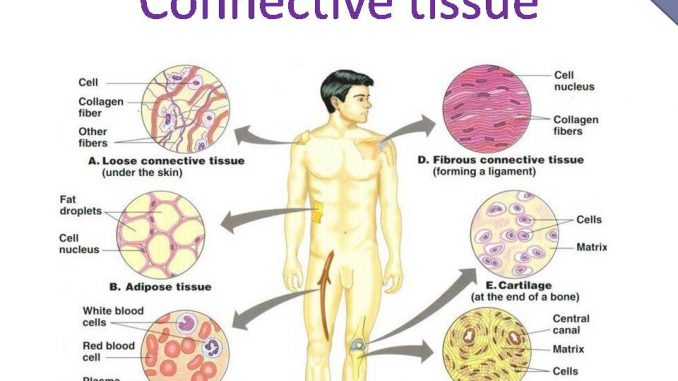
This tissue not only connects different parts but also performs certain other important functions. WBCs form a defence system and protect from foreign antigens. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions.
MUSCLE TISSUE Functions jobs. Blood supports growth by distributing nutrients and hormones and by removing waste. Identification of foreign organisms and removal of pathogens.
1 Conducts impulses to and from body organs via neurons The 3 Elements of Nervous Tissue 1 Brain 2 Spinal cord 3 Nerves IV. Describe the structural characteristics of erythrocytes and how these characteristics relate to gas. Different leukocytes had different sizes but generally each is between 1020 µm.
Describe the components of plasma their relative amounts and their functions. Name the two major components of blood and the percentage of each by weight. Blood is a liquid connective tissue that contains cellular elements blood cells and fluid matrix plasma.
The cells of blood tissue are classified as erythrocytes leukocytes and thrombocytes. Each type of tissue differ from each other in structure which in turn determines its function. These cells deliver oxygen to the cells and remove carbon dioxide.
The primary function of blood is to deliver oxygen and nutrients to and remove wastes from the body cells. Blood helps in the transportation of different substances throughout the body. Dense Regular Connective Tissue.
Name the average volume of blood in a human. Describe the major functions of blood. It has a liquid matrix called blood plasma in which are suspended various blood corpuscles.
Epithelial Connective Muscle and Nervous. Epithelial Epithelial tissue serves the main purpose of providing protection for our bodys outer surface and the passageways inside our body. Lymph nodes bone marrow and spleen.
Blood Transports Nutrients and Hormones. Plasma contains proteins water hormones salts etc. The layered walls of the small intestine provide a good example of how tissues form an organ.
Primarily parallel collagen fibers. Blood Provides the Bodys Cells with Oxygen and Removes Carbon Dioxide Blood absorbs oxygen from air in the lungs. Some tissues help in transportation such as the blood which is a connective that helps in transportation of the cells needed to supply oxygen and also transport other nutrients in the body Some tissues enable humans to move carry loads and facilitate respiration such as the muscular tissue.
NERVOUS TISSUE Functions jobs.
Connective Tissue Characteristics Functions And Types Online Biology Notes

4 1 Types Of Tissues Anatomy Physiology
Connective Tissues Functions Types Characteristics Components Connective Tissue Cells Fibers
0 Comments